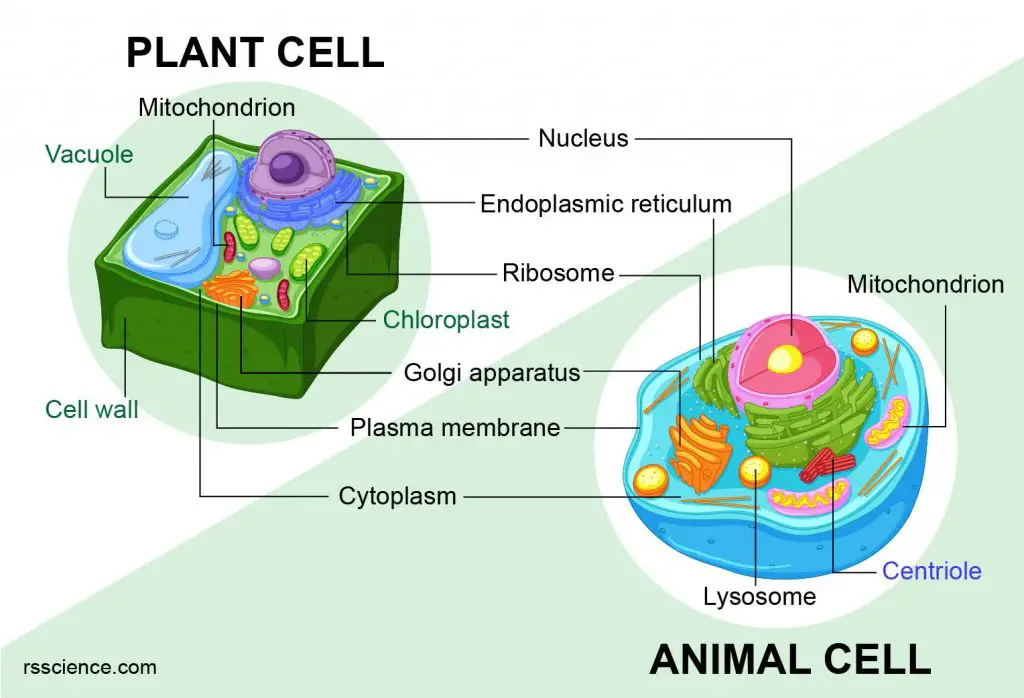
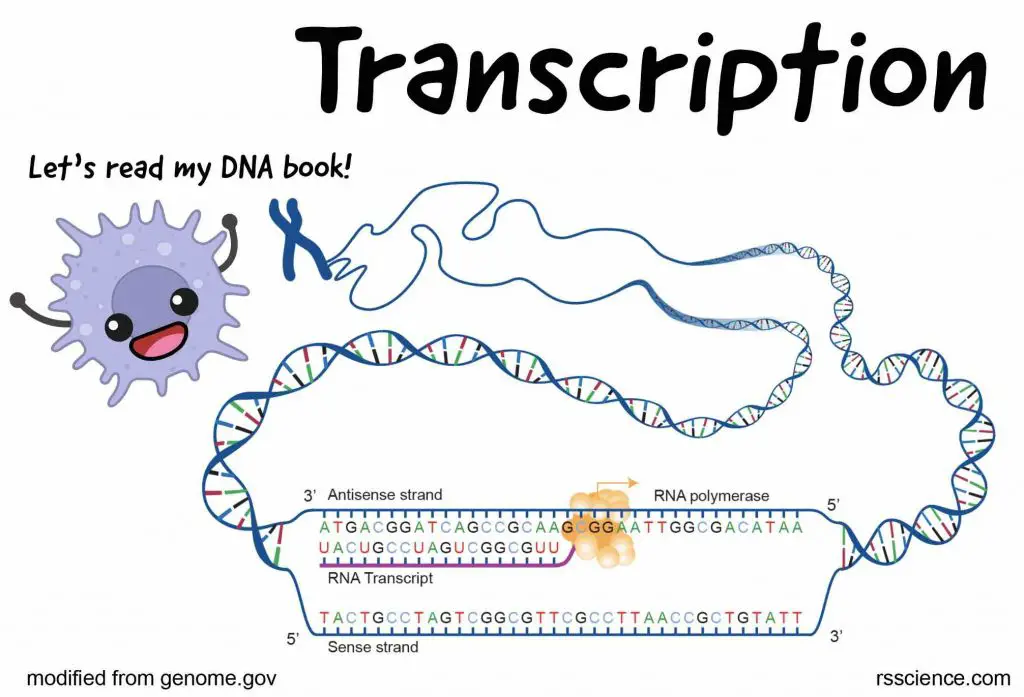
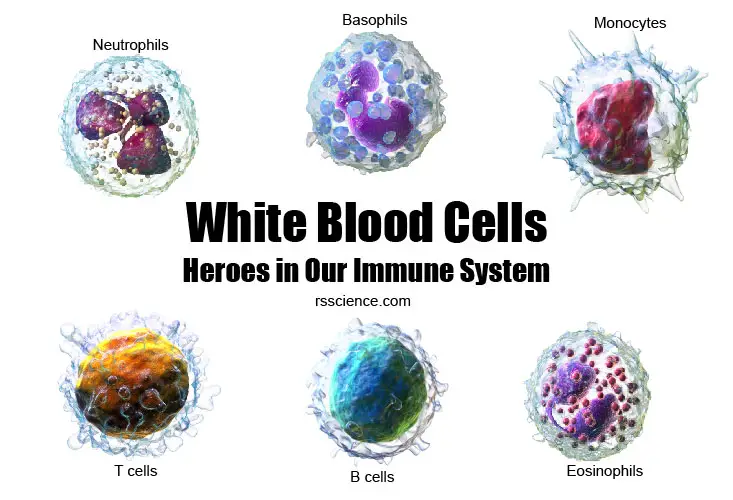
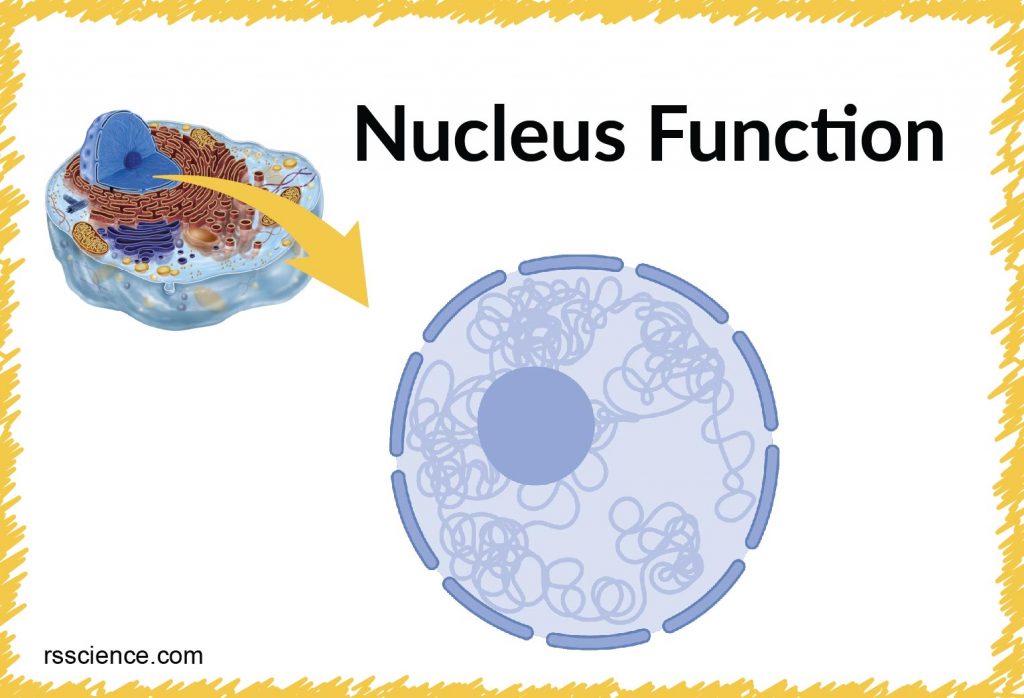
Animal vs. Plant cells – Similarities, Differences, Chart, and Examples
Animal and plant cells are eukaryotic cells. They all have nuclei, cell membranes, and organelles (ER, Golgi, ribosomes, and mitochondria). The structures only in plant cells are the cell wall, chloroplast, and vacuole.