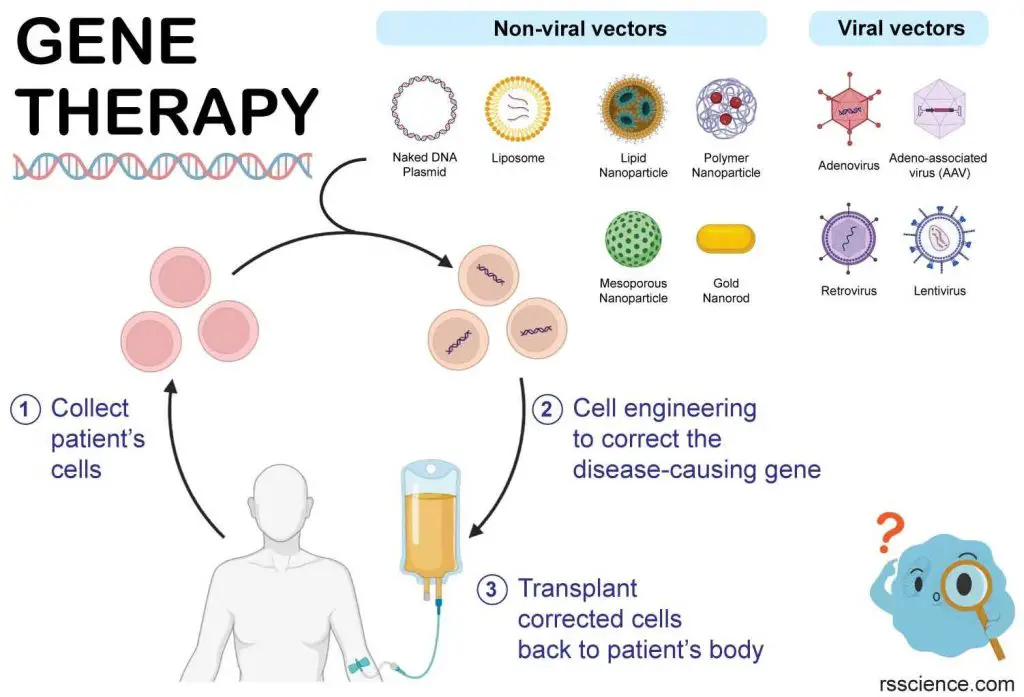
Gene Therapy: A Promising Biotechnology for the Treatment of Genetic Diseases and Cancers – Basic Introduction
Gene therapy is a medical treatment that involves introducing or altering genes within a person’s cells to treat genetic disease and some types of cancer.